Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being. Whether you have diabetes, prediabetes, or are simply keen on monitoring your health, understanding the normal blood sugar levels chart can help you manage your glucose effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Blood sugar levels fluctuate based on various factors including diet, physical activity, and overall health.
- Understanding the normal blood sugar levels chart is essential for managing diabetes and maintaining overall health.
- Different age groups and conditions require different blood sugar level targets.
- Regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments can help maintain normal blood sugar levels.
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels?
Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, refer to the amount of glucose present in your blood. Glucose is a primary source of energy for the body’s cells and is obtained from the foods you eat. The levels of blood glucose are regulated by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels for Adults
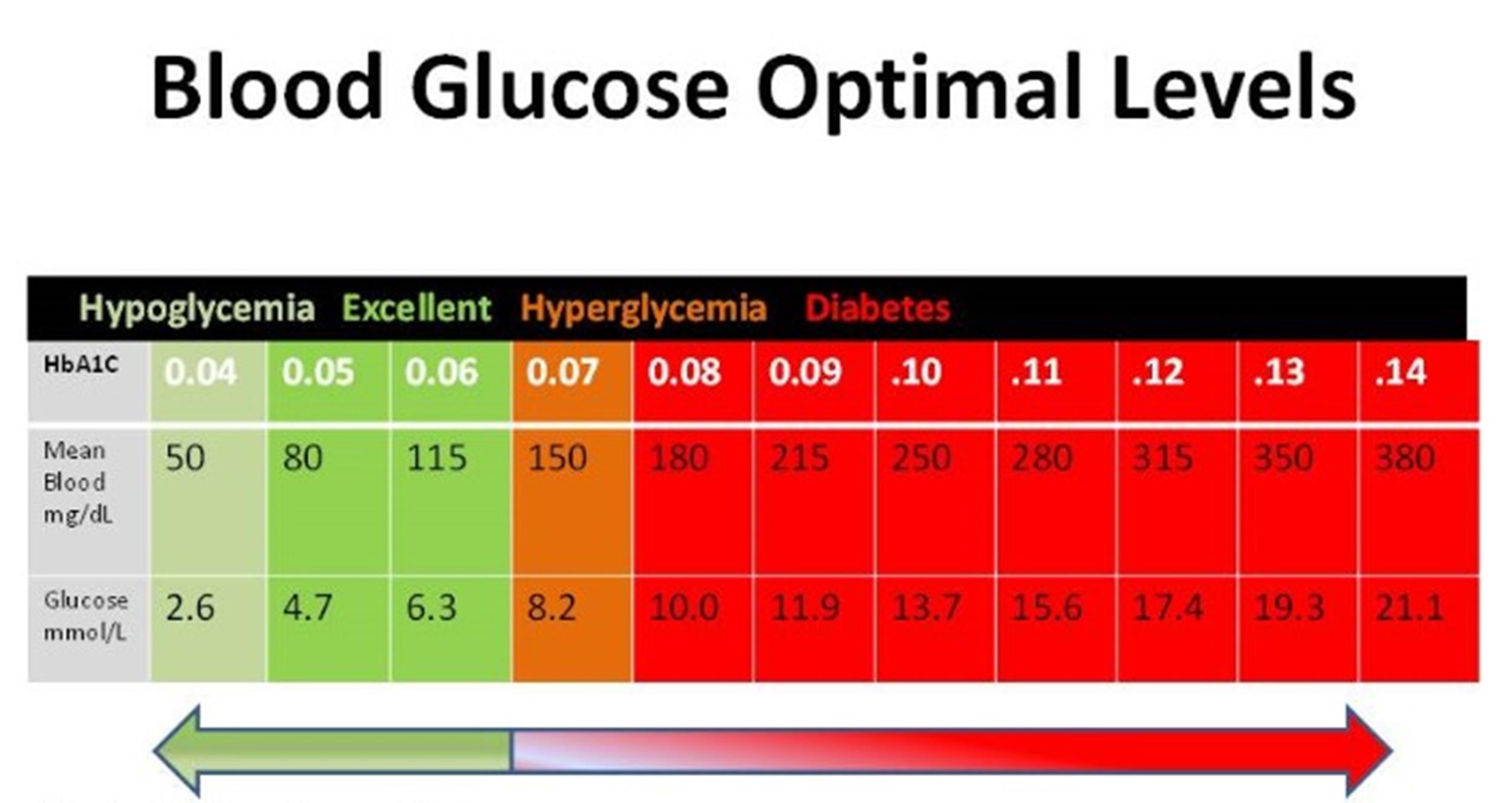
For most adults, normal blood sugar levels are typically:
- Fasting (before meals): 70-99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter)
- Two hours after meals: Less than 140 mg/dL
- Random (any time of the day): Less than 200 mg/dL
Normal Blood Sugar Levels for Children
Children generally have slightly different blood sugar targets compared to adults:
- Fasting: 70-100 mg/dL
- Two hours after meals: Less than 140 mg/dL
- Random: Less than 200 mg/dL
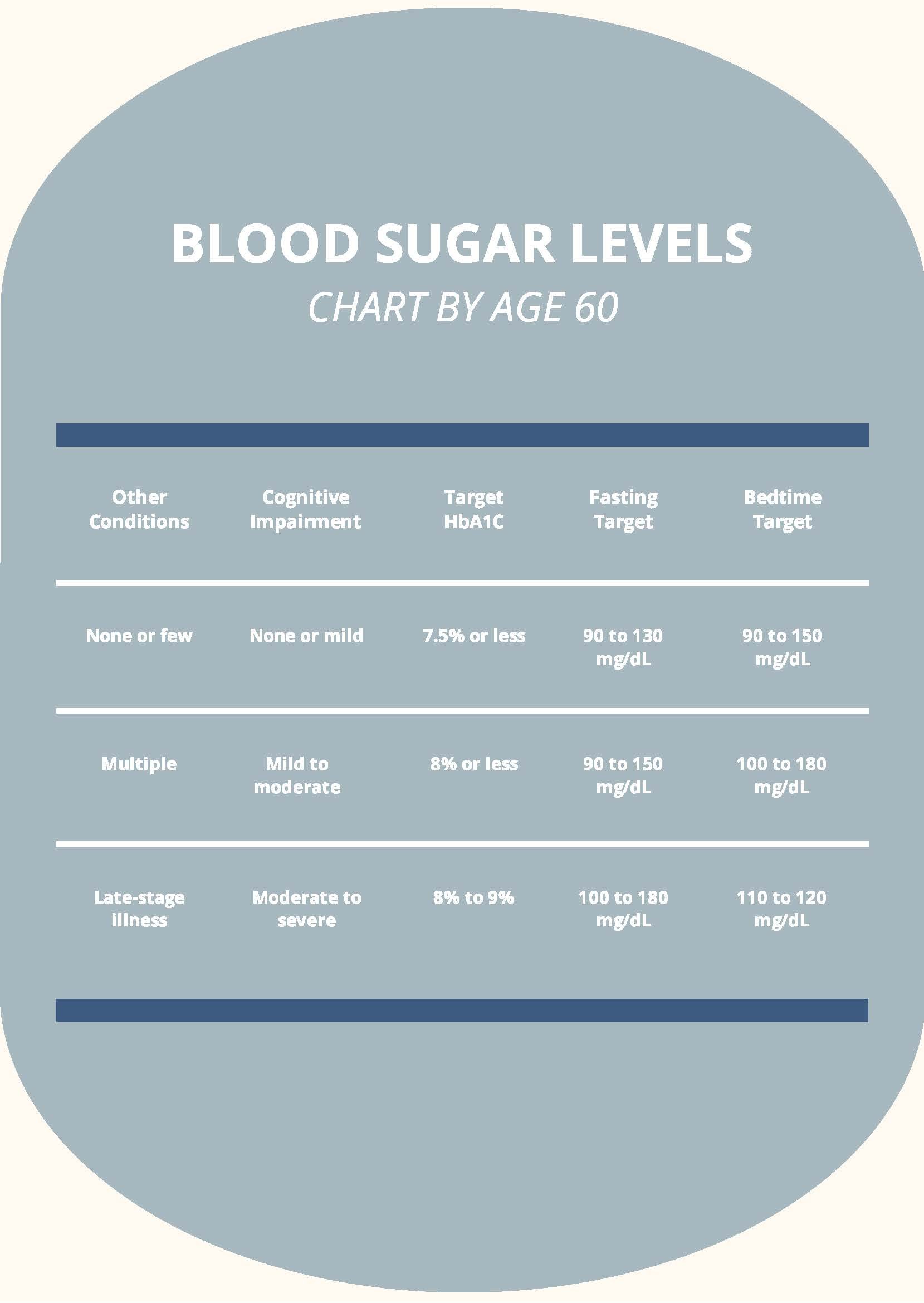
Normal Blood Sugar Levels for Pregnant Women
Pregnancy can affect blood sugar levels, making it crucial to monitor them closely:
- Fasting: 60-95 mg/dL
- One hour after meals: Less than 140 mg/dL
- Two hours after meals: Less than 120 mg/dL
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence your blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: Carbohydrates, sugars, and fats can significantly impact blood glucose levels.
- Physical Activity: Exercise can lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity.
- Medications: Certain medications, including insulin and oral hypoglycemics, can affect blood sugar.
- Stress: Both physical and emotional stress can cause blood sugar levels to rise.
- Illness: Infections or other illnesses can also cause fluctuations in blood glucose.
How to Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential to ensure they remain within the normal range. Here are some common methods:
Home Glucose Monitoring
Using a glucose meter, you can check your blood sugar levels at home. This involves pricking your finger to obtain a small blood sample, which is then placed on a test strip and read by the meter.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM systems use a small sensor inserted under the skin to continuously monitor glucose levels. This method provides real-time data and can alert you to highs and lows.
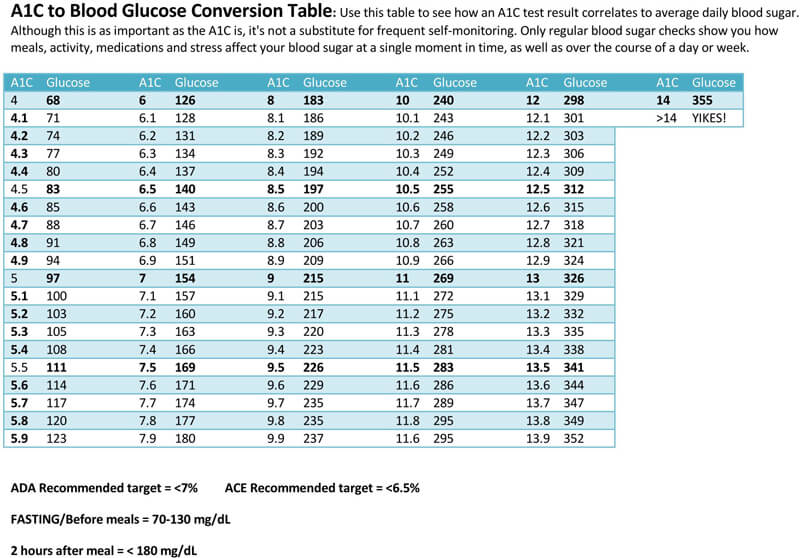
HbA1c Test
The HbA1c test measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It is a valuable tool for assessing long-term glucose control.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Here are some tips:
Healthy Eating
Adopt a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Limit your intake of refined sugars and processed foods.
Regular Exercise
Engage in regular physical activity such as walking, swimming, or cycling. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
Medication Management
If prescribed, take your medications as directed by your healthcare provider. This may include insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents.
Stress Management
Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises to help keep your blood sugar levels stable.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience symptoms such as frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, or persistent fatigue, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider. These could be signs of uncontrolled blood sugar levels or diabetes.
Understanding and maintaining normal blood sugar levels is vital for overall health and well-being. By using the normal blood sugar levels chart as a guide, you can take proactive steps to manage your glucose levels effectively. Regular monitoring, a healthy lifestyle, and timely medical intervention can help you achieve optimal blood sugar control.
Remember, always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and recommendations based on your specific health needs.


